

Do you or your partner snore regularly or occasionally? If so, you’re not alone. Studies show that adults between 30 and 60 years old, 72% snore regularly, more commonly in men. After the age of 60, around half of all people snore regularly. Snoring can be an embarrassment or annoyance for most people, but for others, it can indicate an underlying health issue. Snoring occurs when air passes through your airway when partially blocked, causing tissues at the top of your airway to touch each other and vibrate. Trying various tips can help you learn how to stop snoring while sleeping, and if you have concerns, it’s always best to talk with your doctor.
Dr. Joshua Goldberg’s team of ears, nose, and throat specialists in Willow Grove, PA, is exceptional. They collaborate closely to design personalized treatment plans for each patient, drawing upon their extensive experience and specialized training. Dr. Goldberg and his team’s focus on providing unmatched patient care has earned the trust of physicians throughout the Bucks and Montgomery County, PA, region, including those in surrounding communities.

brushing teeth
Adjusting Bedtime Routines
You can reduce or even eliminate your snoring by making simple adjustments at night.
Did you know that your sleep position can affect your likelihood of snoring? Sleeping on your back can make you snore more often. On the other hand, sleeping on your side, also known as the lateral position, can reduce snoring. Interestingly, the position of your head may play a more significant role than your body position. When you turn your head to the side, you will snore less. If you’re a back sleeper and notice you snore, try to train yourself to sleep on your side. You can also use pillows to help you maintain a comfortable side position throughout the night.
There are many options available for those who suffer from snoring. Anti-snoring mouthpieces are a popular choice for how to stop snoring, although they can take some time to get used to since they are larger and sit in the mouth all night. These mouthpieces are sold over the counter as a mouthguard and typically come in two different types. Interestingly, anti-snoring dental devices can also be helpful for mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. However, it is essential to remember that you should see an ENT if you suspect you have sleep apnea.
If you’re looking for a way to improve your breathing and reduce snoring while sleeping, consider trying internal or external nasal dilators. The design of these tiny devices is to open up your nasal passage so airflow improves, which is a way on how to stop snoring. You can find them easily in most drug stores or online, and they’re quite affordable. Both types of dilators use tension to open up the nasal passages, but the external dilator sticks to the outside of your nose
while you insert the internal one into your nostrils. Studies have shown that both dilators can be effective, but internal dilators tend to work better overall. For how to stop snoring, give nasal dilators a try.

breaking cigarettes
How to Stop Snoring with Lifestyle Changes
If you still find it challenging to stop snoring, consider making more substantial lifestyle adjustments.
Losing weight is often recommended as one of the first and most essential treatments on how to stop snoring. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute gives a helpful chart based on your height, weight, and waistline to determine if you have a healthy weight. If you fall into the nearly 74% of Americans who are overweight or obese, consider reducing your body weight to reduce both snoring and obstructive sleep apnea symptoms. However, it’s important to approach weight loss healthily. Avoid crash diets and follow the Centers for Disease Control’s suggestions for eating a healthy diet and incorporating physical activity into your life.
Did you know that smoking cigarettes can increase snoring? According to the National Library of Medicine’s Biotech Information, it’s true. Quitting smoking is a suitable method on how to stop snoring. It’s worth considering if you or your loved ones are having trouble with snoring.
If you’re someone who tends to snore, you might want to think twice about drinking alcohol before bed. Not only does alcohol increase snoring, but it can induce sleep apnea in people who don’t have the disorder. It’s important to note that your snoring could be heavier if you tend to have multiple drinks. If you cut back on the alcohol and that doesn’t reduce your snoring, stop drinking three hours before bed or stop the liquor intake altogether.

Otolaryngologist
When to See an ENT to Stop Snoring
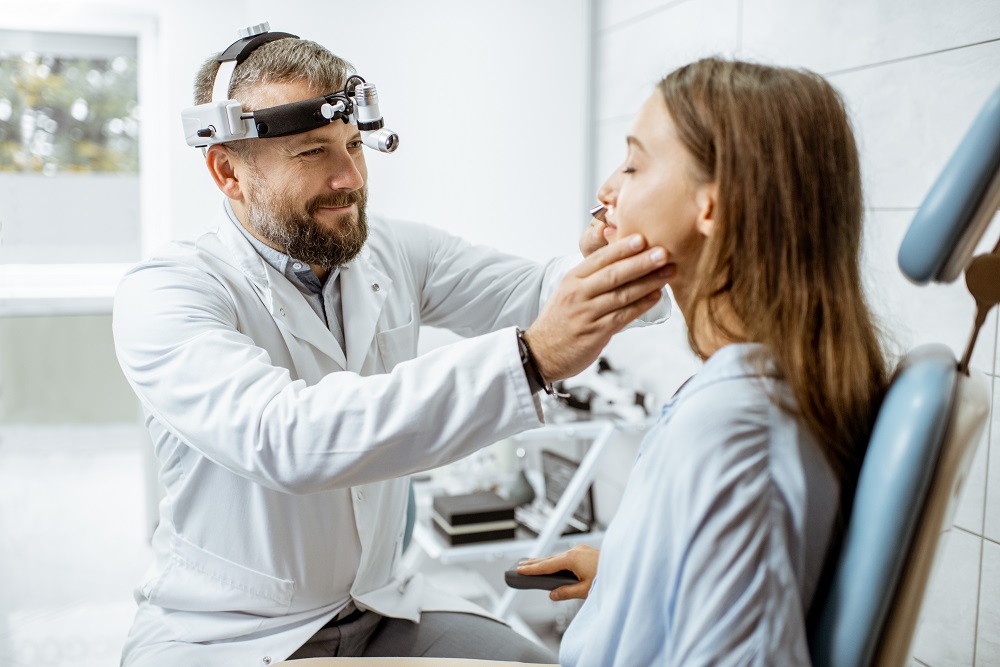
If your snoring persists despite your best efforts to address it, an underlying medical issue may be the cause. You may have obstructive sleep apnea if you experience other symptoms, such as gasping or choking while asleep, daytime tiredness, morning headaches, or feeling unrefreshed upon waking. In this case, seeking medical attention from a doctor who can diagnose the condition and suggest appropriate treatment is important. Addressing obstructive sleep apnea can significantly reduce or even eliminate your snoring while improving your overall health and well-being.
Contact Dr. Joshua Goldberg at (215) 659-8805 or visit his website to learn more information. How to stop snoring is vital for your health as well as your relationships. Don’t delay. Call Dr. Goldberg today!





