

Have you ever experienced a persistent burning sensation in your mouth, as if you’ve just sipped scalding hot coffee, even though you haven’t consumed anything? If so, you might be dealing with a condition known as Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS). This mysterious and often frustrating condition affects countless individuals worldwide, yet it remains widely misunderstood. In this blog post, we’ll dive into what Burning Mouth Syndrome is, its potential causes, symptoms, and how it can be managed.
Burning Mouth Syndrome is a chronic condition characterized by a burning or scalding sensation in the mouth, often without any obvious cause. The discomfort can affect the tongue, lips, gums, palate, throat, or the entire mouth. For some, the sensation is mild and intermittent, while for others, it can be severe and persistent, significantly impacting their quality of life.
BMS is more common in middle-aged or older adults, particularly women going through menopause, though it can affect anyone. Despite its prevalence, diagnosing BMS can be challenging because it often overlaps with other oral health issues or systemic conditions.

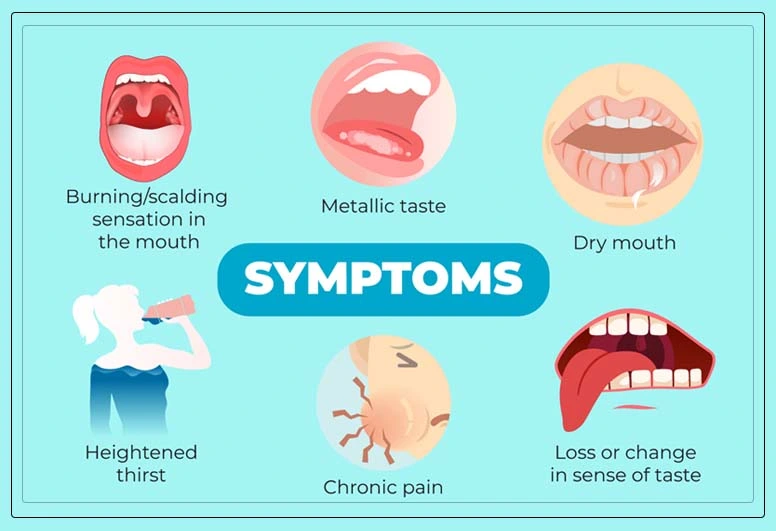
The primary symptom of BMS is, of course, a burning sensation in the mouth. However, this condition can also present with other accompanying symptoms, such as:
The burning sensation may fluctuate throughout the day, often worsening as the day progresses. Some people report temporary relief while eating or drinking, which can make the condition even more perplexing.

The exact cause of BMS is not fully understood, which is why it’s often referred to as a “syndrome” rather than a disease. However, researchers have identified several potential contributing factors, which can be categorized into primary and secondary causes:
When no underlying medical or dental cause can be identified, the condition is classified as primary BMS. It is believed to be related to nerve dysfunction or damage in the oral cavity, possibly involving the nerves responsible for taste and pain.
Secondary BMS occurs when the burning sensation is linked to an underlying condition or factor, such as:

Diagnosing BMS can be a process of elimination. Your healthcare provider or dentist will likely start by reviewing your medical history, conducting a physical examination, and ruling out other potential causes of your symptoms. They may also order blood tests to check for nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, or other systemic issues.
In some cases, a referral to a specialist, such as an oral pathologist or neurologist, may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for BMS, several treatment options can help manage the symptoms and improve your quality of life. The approach will depend on whether your BMS is primary or secondary:
If an underlying cause is identified, treating that condition often alleviates the burning sensation. For example:
When no specific cause is found, treatment focuses on symptom management. Options may include:
Living with BMS can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to cope with the condition:
Burning Mouth Syndrome is a complex and often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact daily life. While the road to diagnosis and treatment may be frustrating, understanding the potential causes and exploring management strategies can provide relief and hope. If you suspect you have BMS, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. With the right approach, you can take control of your symptoms and reclaim your comfort.
Have you or someone you know experienced Burning Mouth Syndrome? Share your story in the comments below—it might just help someone else feel less alone in their journey.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. If you’re experiencing symptoms of Burning Mouth Syndrome, consult a Dr.Joshua for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.





